The deep oil and gas has the geologicalcharacteristics of high temperature, high pressure, high maturity and proximal hydrocarbon accumulation, which is conducive to the generation and accumulation of hydrocarbon. The present exploration of Jurassic in the deep part of Shengbeisag centers in Tuha oilfieldhas a low exploration level. This study conducted multiple experiments of thin section identification, organic geochemistry, and NMR and systematically evaluated the geological conditions and major controlling factors for hydrocarbon accumulation in the coal measure strata. The results show that multiple sets of coal-measure source rocks have developed in the Jurassic strata in the center Shengbei sub-sag. Tight sandstones have poor physical properties and complex pore structures. High-permeability zones and anomalous zones of nano-scale pores have developed in the deep part. The microscopic storage space and connectivity of the reservoirs were improved due to the dissolution of fluids in coal measure strata. The occurrence of high-quality reservoirs is significantly controlled by source rocks, and both the former and the latter are characterized by adjacent sources and reservoirs and short-distance migration and accumulation.
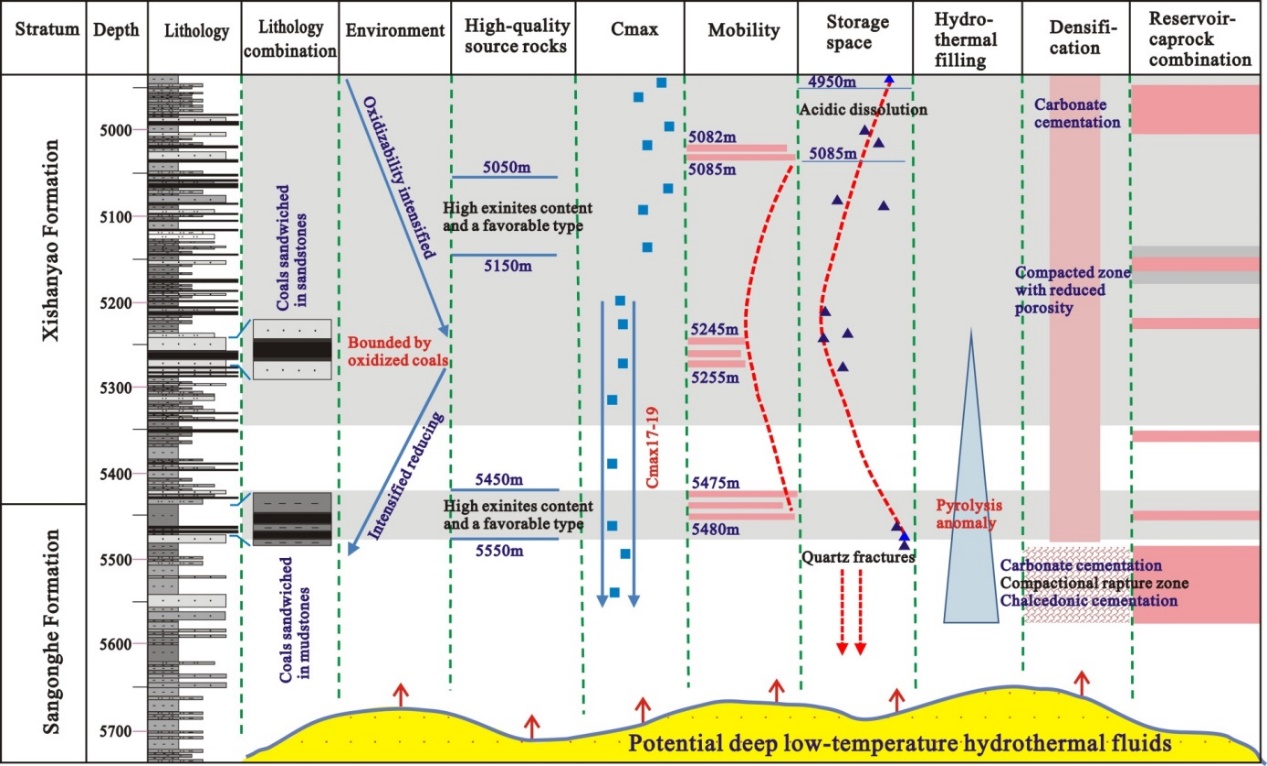
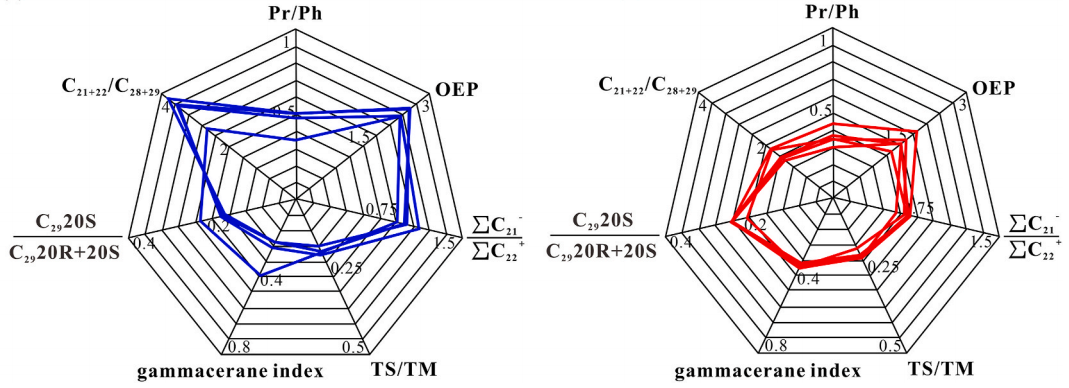
Fig. 1. Geological factors in the hydrocarbon accumulation in well QT-1 in the Shengbei sub-sag.
Using thermal simulation and molecular simulation methods, the study took the fourth member of the Shahejie Formation in the Leijia area, Liaohe Depression as an example, based on the calculation ofhydrocarbongeneration pressure and oil-source correlation, to explore the difference of hydrocarbon generation between argillaceous dolomite and mudstone and its influence on tight oil source. The hydrocarbon generation characteristics of argillaceous dolomite and mudstone are significantly different. Mudstone starts hydrocarbon generation later and has a shorter hydrocarbon generation cycle, while argillaceous dolomite starts hydrocarbon generation earlier and has a longer hydrocarbon generation period. Due to the difference in hydrocarbon generation characteristics, when the burial depth is below 3000 m, the oilgeneration overpressure in the mudstone is smaller than that in argillaceous dolomite, and the tight oil in the argillaceous dolomite reservoir is mainly generated by and stored in the argillaceous dolomite itself. When the burial depth exceeds 3000 m, the oil-generation overpressure in the mudstone surpasses that in argillaceous dolomite, and the tight oil has mixed source characteristics.
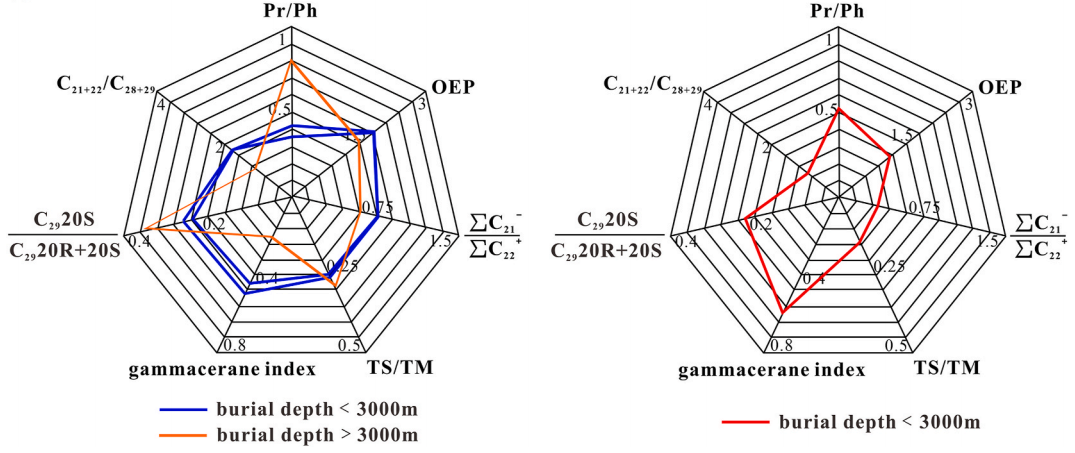
Fig. 2. Biomarker characteristics of source rocks. (a) Mudstone; (b) argillaceous dolomite.
Paper Information:
CITATION 1:Weiming Wang, Tingting Li, Dongsheng Xiao, Bo Wang, Yuzhong Yang, Yangchen Zhang, Weihao La, Jiang He. Geological conditions and controls on accumulation of tight sandstone gas, deep part of the Shengbei sub-sag, Turpan-Hami basin, NW China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 158(PA): 106513.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106513.
CITATION 2:Weiming Wang, Ketao Zheng, Shuangquan Huang, Qunyi Wang, Guoqi Feng, Yue Su, Jijun Li. Difference of hydrocarbon generation between argillaceous dolomite and mudstone and its influence on oil source: A case study of the Es4 in the Leijia area, Liaohe depression. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 237(2024)212805.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoen.2024.212805.
CITATION 3:Weiming Wang, Haoyu Ma, Yajing Li, Zhuo Yi, Zhen Li, Youguo Yan. Salt-Induced Coil−Globule Transition of Sulfonate-Modified HPAM is Affected by the Branched Chain Length. Langmuir 2023 39 (42),14969−14976.https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c01832.